Suffering from Plantar Fasciitis?
Find out how Plantar Fasciitis Embolization can help you.
Plantar fasciitis embolization is a minimally invasive procedure performed by National Vascular Physicians ideal for those experiencing pain from plantar fasciitis pain that is impacting their quality of life.
What is Plantar Fasciitis?
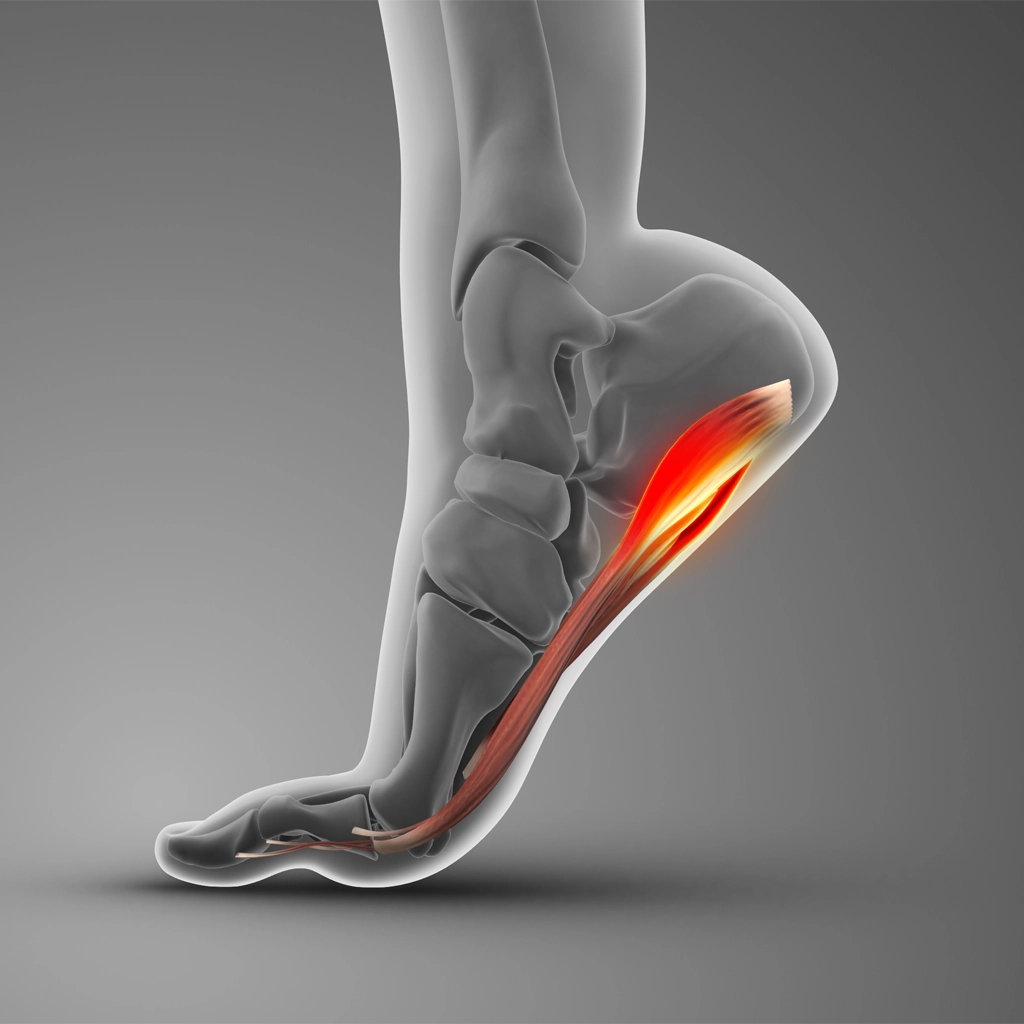
The fascia is the thick band of tissue on the bottom of the foot that connects the heel bone to the toes. When the fascia is injured and becomes inflamed, it can be extremely painful. It is thought to be the result of repeated microtrauma to the heel.
Who is at risk?
- Women are more at risk than men
- Athletes, especially runners
- Those with a job that requires prolonged standing
What does the research say?
Plantar fasciitis embolization is a safe and clinically proven1 outpatient procedure with an excellent profile and safety record.
- Rozil Gandhi, et al. Early outcomes of transcatheter arterial embolization using imipenem/cilastatin for plantar fasciitis refractory to conservative therapy. Br J Radiol 2024 Feb 28;97(1155:544-548.

Plantar Fasciitis symptoms
- Sharp pain in the heel or bottom of the foot
- Pain that increases with activity and decreases with rest
- Tenderness and swelling
Is Plantar Fasciitis Embolization right for me?
You may be a candidate if you:
- Have plantar fasciitis and conservative treatment has not been effective
- Wish to avoid surgery
- Do not have the time or ability to wait for the condition to heal on its own
Key Advantages
- PFE is safer than surgery
- Requires only a single treatment session
Benefits
- High treatment success rates
- Same day procedure
- Quick recovery
- No general anesthesia required
- Lower risk than surgery
Although PFE complications are extremely rare, any medical procedure carries some degree of risk. Despite the low risk factor, it is important to understand the potential complications associated with plantar fasciitis embolization, which include:
- Infection
- Non-target embolization
Other Treatment Options
Surgical Treatments
A surgery called plantar fasciotomy is sometimes performed to relieve pressure and restore blood flow to the heel. Unfortunately, up to 44% of patients still experience swelling and tenderness up to 10 years after having this surgery.1 There are also complications after surgery, including instability, nerve injury and recurrent heel pain.
Other Procedures
Less invasive options such as extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) or high intensity laser therapy (HILT)/low-level laser therapy (LLLT) are available as less invasive options to surgery. Unlike plantar fasciitis embolization, these options require multiple treatment sessions and have a success rate between 74-76% (ESWT)2 and 51-73% (laser therapy).3
Medical Treatments
- Pain and anti-inflammatory medications
- Heat and/or cold packs
- Physical therapy
- Assistive devices
- Rebekah Gibbons et al. Evaluation of Long-Term Outcomes Following Plantar Fasciotomy. Foot Ankle Int. 2018 Nov; 39(11):1312-1319.
- R. Scheuer et al. Approaches to optimize focused extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) based on an observational study of 363 feet with recalcitrant plantar fasciitis. International Journal of Surgery Volume 27, March 2016, Pages 1-7.
- Dovile Naruseviciute et al. The effect of high-intensity versus low-level laser therapy in the management of plantar fasciitis: randomized participant blind controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2020 Aug; 34(8): 1072-1082.