Spine & Joint Care
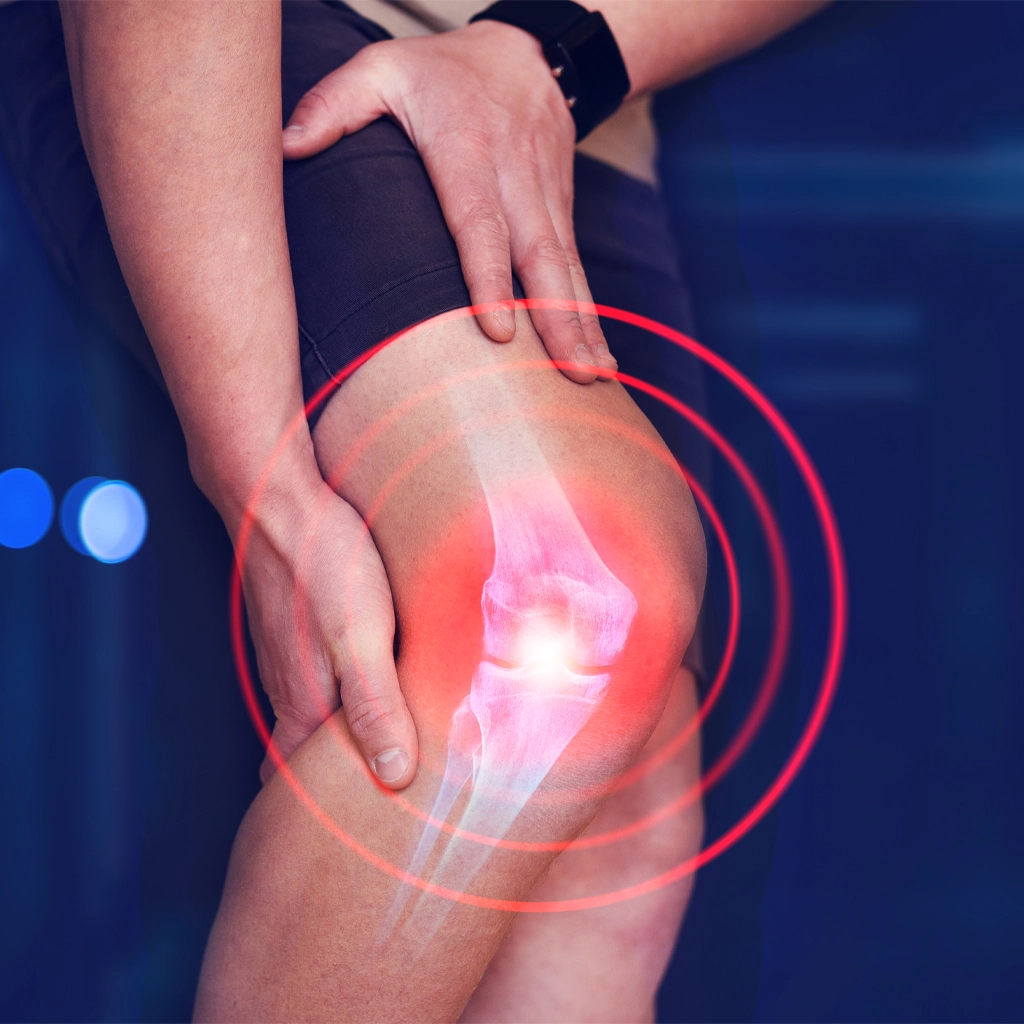
Suffering from Knee Arthritis?
Find out how Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE) can help you.
GAE is a same-day, minimally invasive procedure that offers highly effective and long-lasting relief of the pain and stiffness caused by chronic joint disease.
Suffering from a Spinal Compression Fracture?
Find out how Kyphoplasty can help you.
Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive surgery used to treat a spinal compression fracture. Spinal compression fractures occur primarily in spinal vertebrae that have been weakened by osteoporosis.
Suffering from Frozen Shoulder?
Find out how Adhesive Capsulitis Embolization can help you.
Adhesive capsulitis embolization is an interventional radiology treatment for frozen shoulder that offers highly effective and long-lasting relief of the pain and stiffness caused by this chronic joint disease.
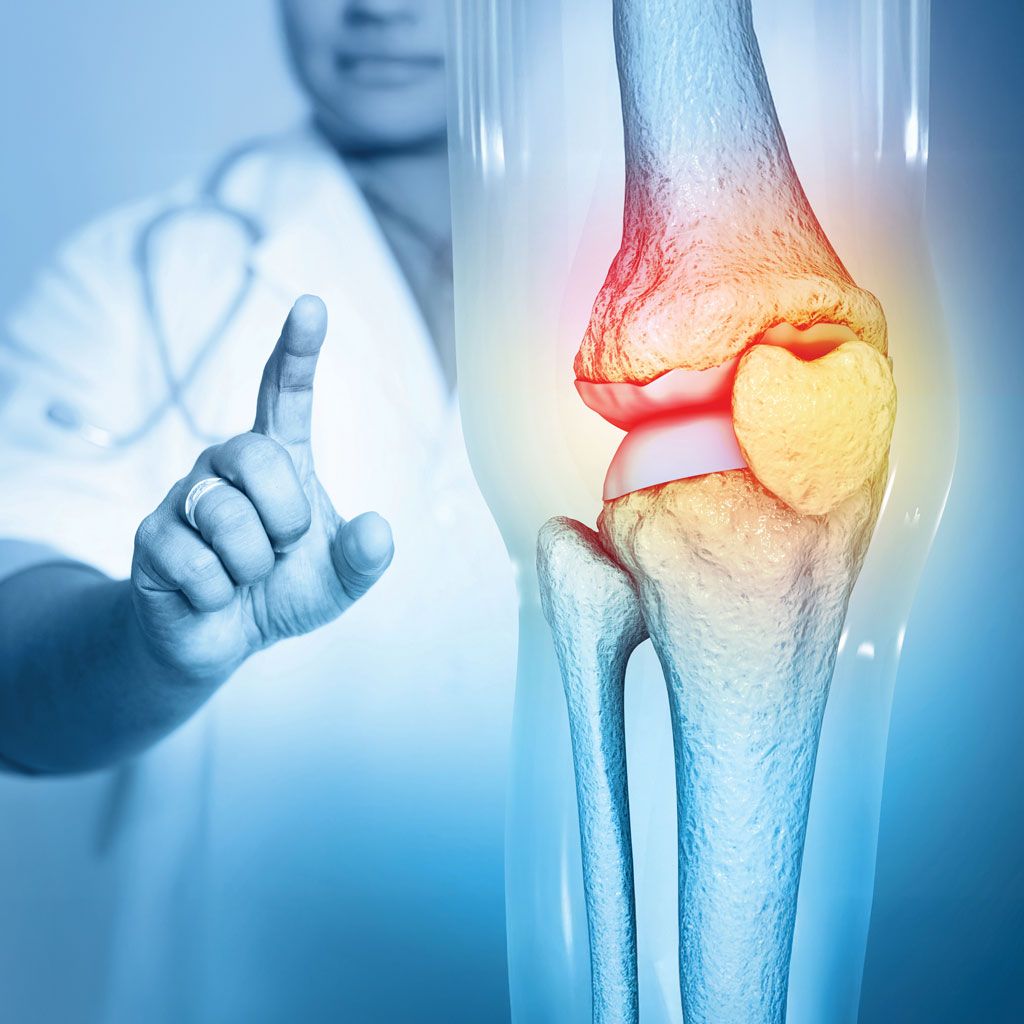
Joint Care: Knee Osteoarthritis
What is Knee Osteoarthritis?
Arthritis is a general term for joint inflammation. Osteoarthritis is the most common type. It often comes with age and affects the hands, knees, and hips.
Who is at risk?
- Increased age
- Increased weight
- Trauma to joint due to repetitive movements such as squatting or kneeling
What does the research say?
Knee osteoarthritis embolization (geniculate artery embolization) is successful in decreasing pain and improving function for patients with knee osteoarthritis
Knee Osteoarthritis Symptoms
- Pain. Affected joints might hurt during or after movement.
- Stiffness. Joint stiffness might be most noticeable upon awakening or after being inactive.
- Joint Tenderness
- Loss of flexibility
- Swelling
Genicular Artery Embolization Treatment for Knee Joint Care
Genicular artery embolization (GAE) is a medical procedure that is used to treat chronic knee pain by blocking blood flow to the knee joint. During the procedure, a small catheter is passed into a vessel through a pinhole in the wrist or groin to deliver small particles into the genicular arteries, which are the blood vessels that supply blood to the knee joint. By blocking blood flow to the knee, inflammation and pain are reduced, leading to improved knee function and reduced pain. The procedure is minimally invasive and the entire outpatient treatment lasts about an hour.
Genicular artery embolization (GAE) has been demonstrated in multiple studies to decrease pain and improve function for the majority of treated patients with knee osteoarthritis.
Is Genicular Artery Embolization Right For Me?
You may be a candidate if:
- You have knee pain or tenderness from osteoarthritis
- Knee stiffness or swelling from osteoarthritis
- Do not want surgery
Key Advantages
Genicular Artery Embolization is a safe treatment option and like other minimally invasive procedures has significant advantages over conventional surgery.
Benefits
- High treatment success rates
- Same day procedure
- Quick recovery
- No general anesthesia required
- Lower risk than surgery
- Potential Risks
Although Genicular Artery Embolization complications are expected to be extremely rare, any medical procedure carries some degree of risk. Despite the low risk factor, it is important to understand the potential complications associated with knee osteoarthritis embolization.
These include:
- Infection
- Non-target embolization
Other Treatment Options
Surgical Treatments
- Knee replacement
Medical Treatments
- Pain and anti-inflammatory medications
- Hot/cold packs
- Assistive Devices
- Canes, splints, walkers
Genicular Artery Embolization Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Are between 40-80 years of age
- Have moderate to severe knee pain
- Are diagnosed with osteoarthritis
- Experience local knee tenderness
- Have resistant or failed conservative treatment (medication, physical therapy, joint injections)
- Current or former smoker
- Advanced arthritis based on an imaging test
- Infection or malignancy
- Are a good candidate for knee replacement surgery
Joint Care: What is a Spinal compression fracture?
- Spinal compression fracture, also known as vertebral fracture, osteoporotic fracture or wedge fracture, is a type of fracture in the spine typically caused by osteoporosis. Cancer spread to the spine can also lead to this type of fracture.
- These fractures are associated with sudden back pain which can lead to chronic pain, deformity and loss of height.
- These fractures are very common and occur in approximately 700,000 people in the United States annually. It is estimated that 25% of all postmenopausal women have had a vertebral compression fracture. Compression fractures should be suspected in anyone over 45 years old with sudden back pain. These fractures can occur after fairly routine activities that slightly strains or jars the back such as lifting a bag of groceries or bending to pick something up off the floor.
Spinal Compression Fracture Symptoms:
- Sudden back pain
- Worsening back pain with standing/walking
- Easing of pain when lying down
- Vertebral deformity – kyphosis
- Height loss
If you are experiencing signs and symptoms of a spinal compression fracture, and are finding it difficult to perform your daily activities and maintain your way of life, contact your primary care physician immediately.
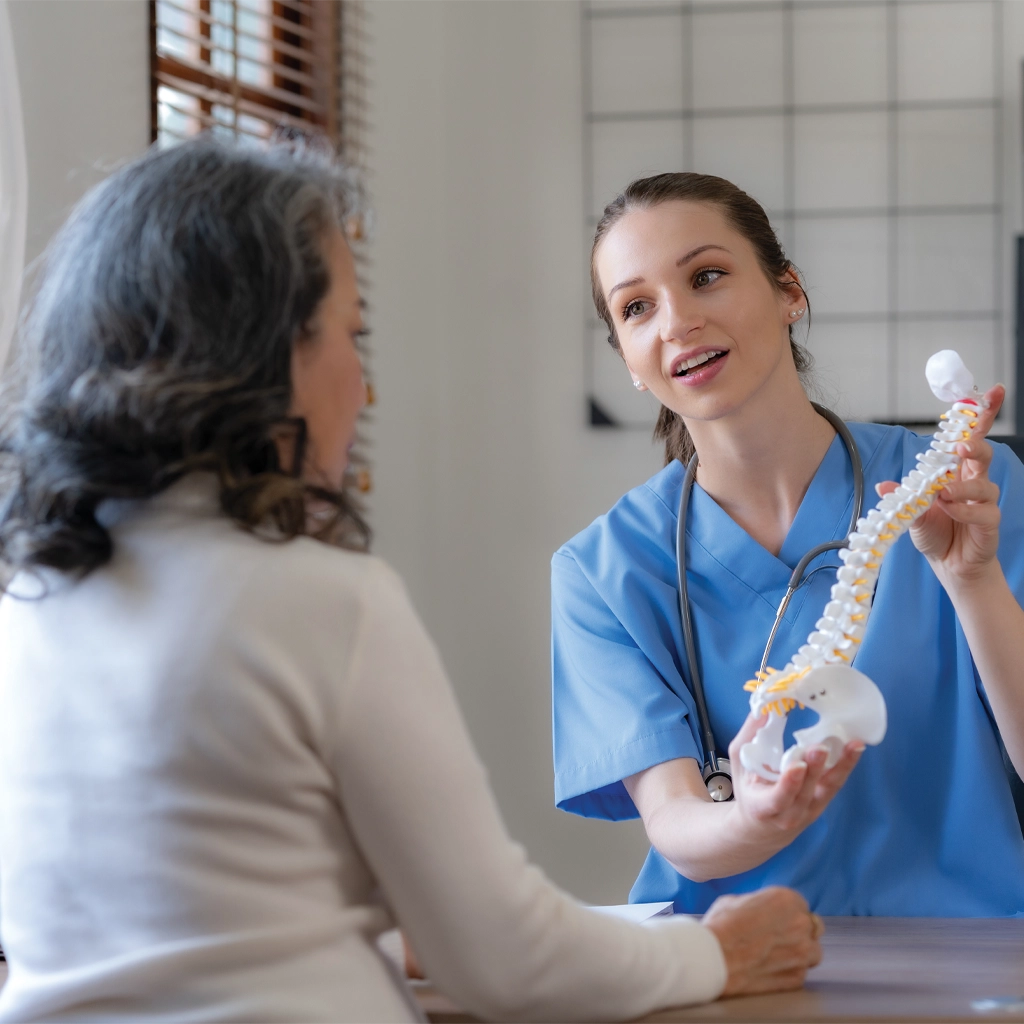

Vertebral Augmentation
Vertebral augmentation, also known as vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure designed to reduce the pain and loss of function associated with spine compression fractures. Vertebral augmentation is typically performed under moderate sedation with the patient asleep but arousable. One of two small needles are advanced under advanced x-ray guidance into the fractured vertebral body. A special balloon may be used to lift up the fractured vertebrae to restore height. Medical cement-like material called polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) is then injected to immediately stabilize and restore strength to the fractured vertebrae. Pain relief is immediate for some patients and most patients see improvement within 48 hours.
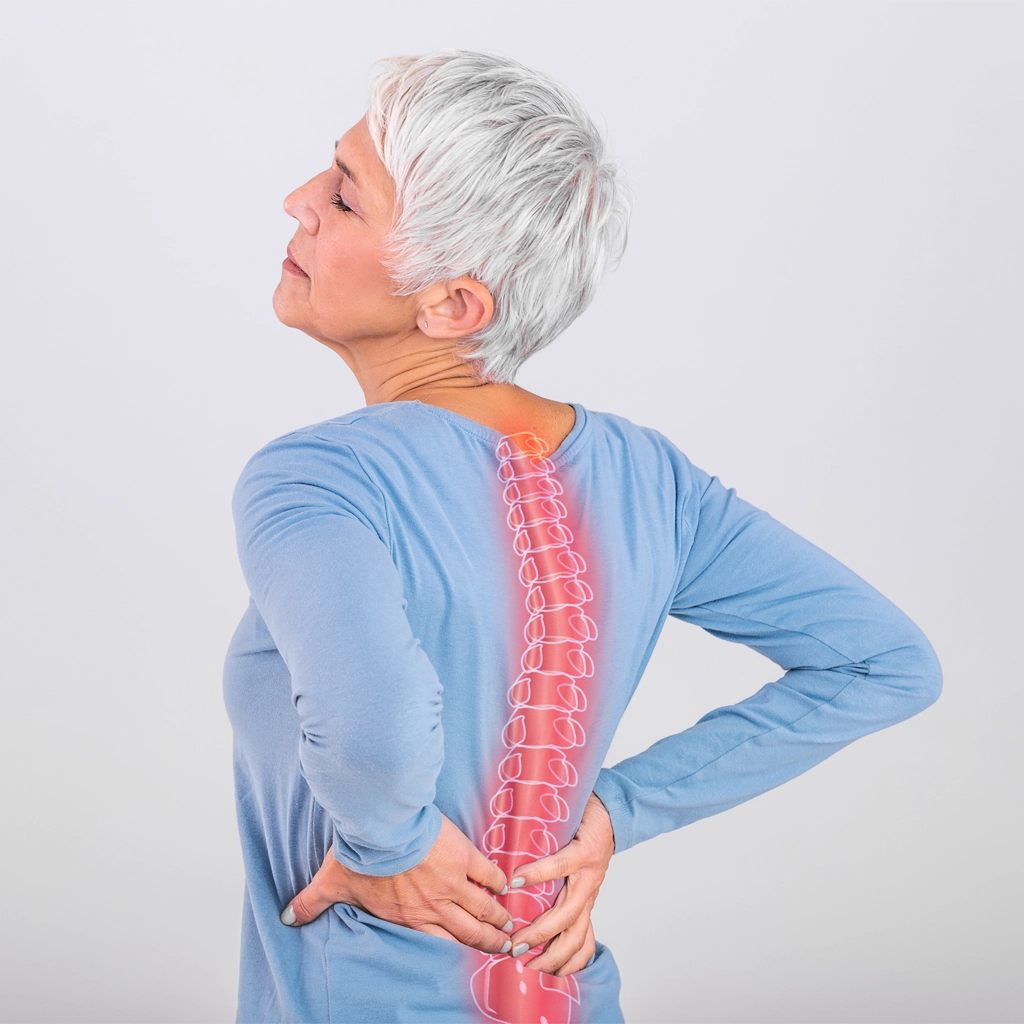
Is Vertebral Augmentation right for me?
You may be a candidate for Vertebral Augmentation if:
- You are experiencing sudden back pain
- You are concerned about long-term consequences of spine compression fracture such as loss of height or vertebral deformity
- Do not want to wear back braces long-term
Benefits
- Multiple research studies demonstrating symptomatic benefit of treatment
- Reduce risk of long-term complications associated with spinal compression fractures
- Same day procedure
- No general anesthesia required
Risks
- Infection
- Allergic reaction to PMMA
- Spinal nerve inflammation
- Disability from spinal cord injury – rare
- Cement causing blockage of lung blood vessels – rare
Other Treatment Options
Medications
Pain medications will help reduce symptoms of spinal compression fractures allowing the fractures to heal on their own. Does not lead to height restoration or reduce risk of vertebral deformity. Addiction risk.
Back bracing
Provides external support to limit motion of fractured vertebrae. Does not allow for immediate pain relief or height restoration. Risk of vertebral deformity in long-term
Spinal fusion surgery
Surgery under general anesthesia where two or more vertebrae are fixed together to keep them from moving until they have a chance to fuse with each other. After an incision is made, metal screws are placed into the vertebrae. The screws are attached to metal plates or rods that are bolted together in the back of the spine. This is often used as the last resort therapy if other treatments fail.
Joint Care: Frozen Shoulder
What is a Frozen Shoulder?
A frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis) occurs when the tissue around the shoulder joint gets thick and tight causing pain and restricted motion.
Who is at risk?
- Shoulder injury (such as a rotator cuff tear), a bone fracture, or shoulder surgery
- Diabetes mellitus
- Immobilized for prolonged periods
- Stroke
- Parkinson disease
What does the research say?
- Frozen shoulder embolization is successful in decreasing pain
- Frozen shoulder embolization is successful in improving range of motion
Frozen Shoulder Symptoms
- Stiff and painful shoulder
- Trouble reaching overhead or around the lower back
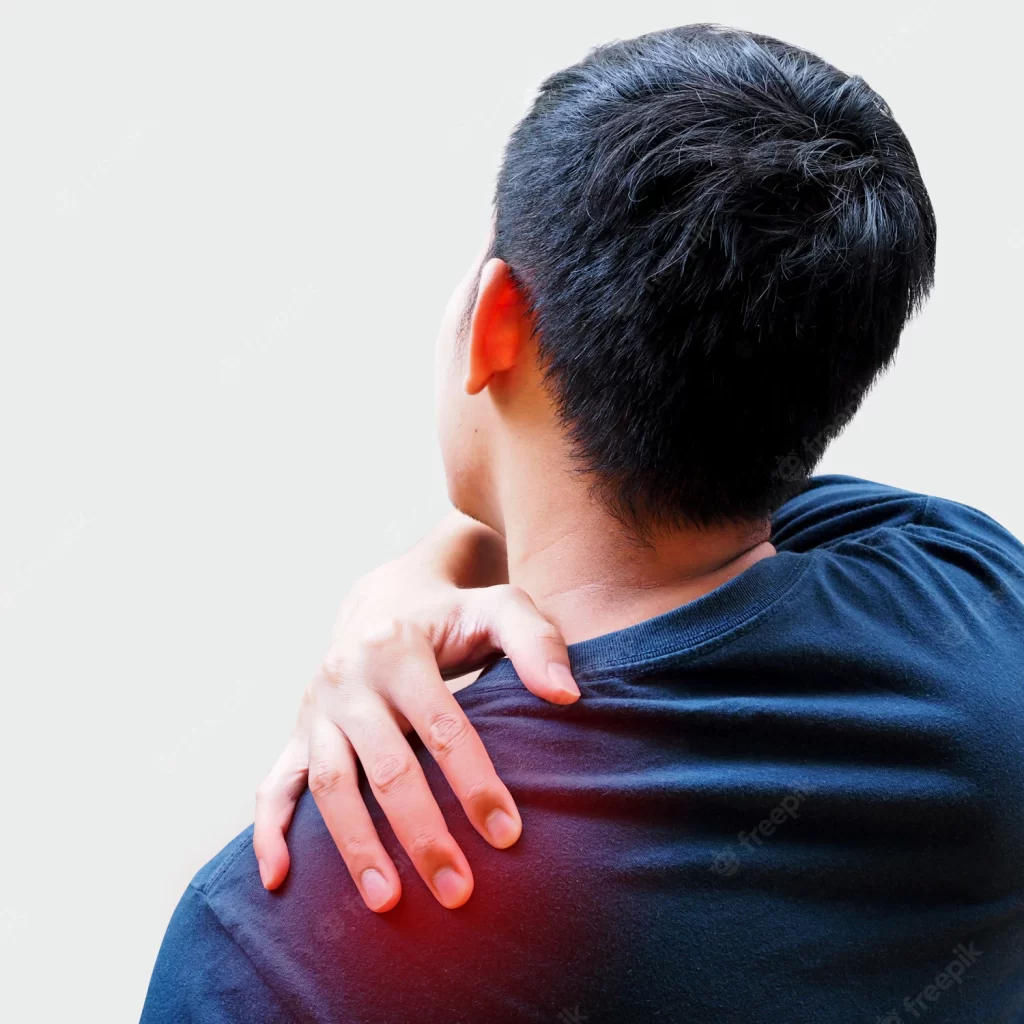

Adhesive Capsulitis Embolization
Adhesive capsulitis embolization is an interventional radiology treatment for frozen shoulder that offers highly effective and long-lasting relief of the pain and stiffness caused by this chronic joint disease. An Interventional Radiologist (IR) passes a catheter (small tube) through a vessel in the wrist or groin using specialized x-ray equipment. Once the catheter is appropriately positioned, the arteries are blocked off using metallic coils and sclerosing agents. The entire joint care treatment typically lasts less than 1 hour and is an outpatient procedure. Recovery typically takes 24-48 hours.
Is Adhesive Capsulitis Embolization for shoulder joint care right for me?
You may be a candidate for Adhesive Capsulitis Embolization if:
- You have pain from frozen shoulders
- You have limited motion from frozen shoulder
Key Advantages
Frozen shoulder embolization is a safe treatment option and like other minimally invasive joint care procedures has significant advantages over conventional surgery.
Benefits
High treatment success rates
Same day procedure
No general anesthesia required
Risks
Although frozen shoulder embolization complications are expected to be extremely rare, any medical joint care procedure carries some degree of risk. Despite the low risk factor, it is important to understand the potential complications associated with frozen shoulder embolization.
These include:
- Infection
Other Joint Care Treatment Options
Surgical Treatment
If other treatments such as pain medications and physical therapy are unsuccessful, surgery may be considered.