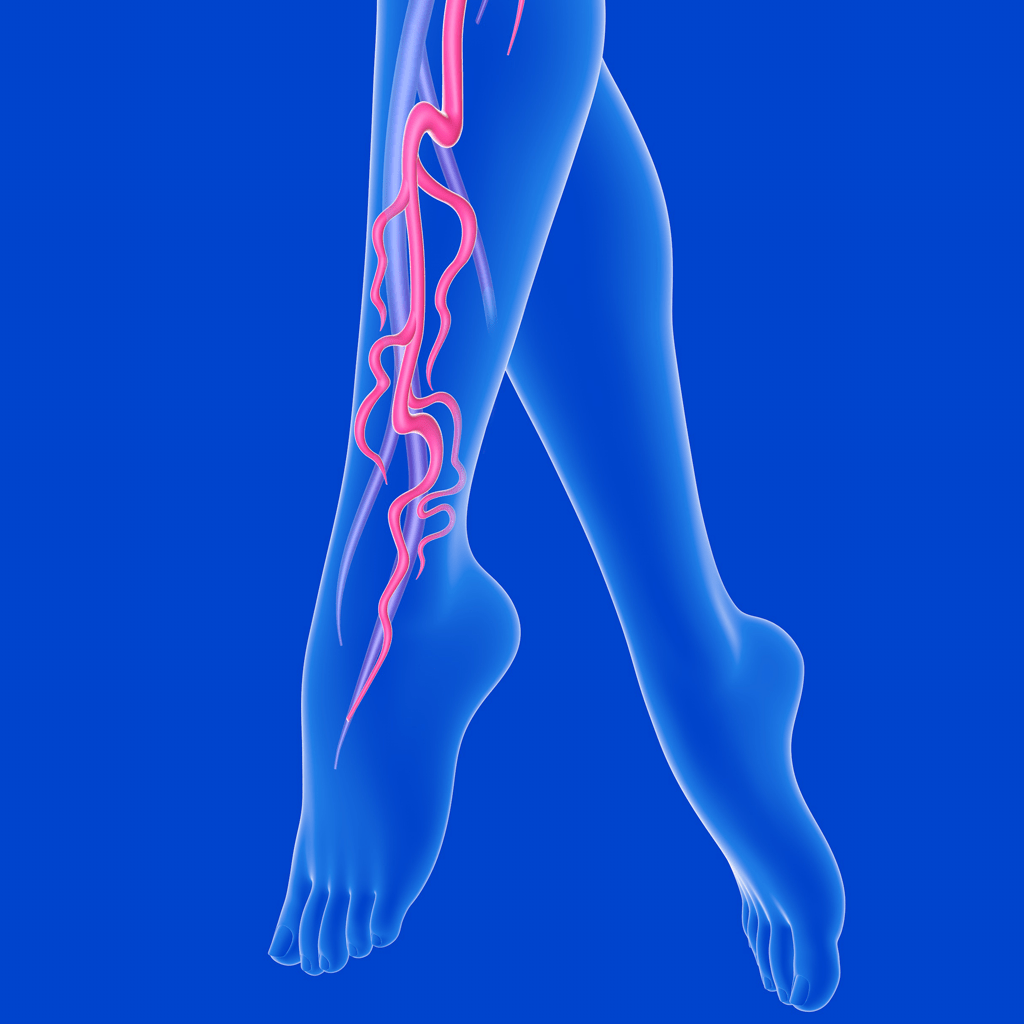
Peripheral Artery Disease
What is Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)?
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a common problem in which narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to the legs and feet. The narrowed arteries are often due to a buildup of calcium and/or fatty deposits in the arteries. Patients can develop symptoms of PAD including muscle pain or cramping with activity such as walking or running, leg wounds, and in some cases pain at rest.
Who is at risk for Peripheral Artery Disease?
-
Increasing age, especially after 50
-
Smoking
-
Diabetes
-
Family history of heart or artery disease
-
High cholesterol levels
What does the research say about Peripheral Artery Disease?
-
Methods to open up arteries through minimally invasive endovascular techniques have improved outcomes for certain types of PAD
-
Early therapy may reduce the risk of limb loss
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) Symptoms
Peripheral artery disease symptoms include:
- Pain with physical activity such as walking
- Relief of pain with rest
- Cramping of buttock, hip, thigh or calf
- Leg hair loss
- Smooth shiny skin of legs and feet
- Sores or ulcers in the legs or feet that do not heal
- Cold or numb legs and/or feet
If you are experiencing signs and symptoms of Peripheral artery disease (PAD), and are finding it difficult to perform your daily activities and maintain your way of life, contact your primary care physician immediately.
Endovascular Treatments
Angiography
Minimally invasive procedure where a small tube (catheter) is inserted into the artery in the groin or wrist. Contrast dye is then injected into the catheter and special x-rays are obtained to see if a vessel is narrowed or blocked.
Angioplasty
Angioplasty may be performed during angiography. If a blood vessel is found to be narrowed or blocked, a small balloon is advanced through the same catheter in the groin or wrist to stretch and open up the narrowed blood vessel. This will increase the blood flow to the affected area.
Thrombolysis
Thrombolysis may be performed during angiography. If a blood clot is found to be the cause of the narrowed or blocked vessel, a clot-dissolving drug or a specialized tool may be infused to dissolve or retrieve the clot.
Atherectomy
Atherectomy may be performed in conjunction with angiography. If a blood vessel is found to be narrowed or blocked due to calcified vessels, a specialized tool may be inserted to remove the calcification to increase blood flow to the affected area.
Stent placement
A stent may be placed during angiography. If a blood vessel is found to be narrowed or blocked and will not stay open after balloon angioplasty and/or atherectomy, a metal tube may be inserted in the narrowed vessel to keep the vessel open.
Is Endovascular Treatment right for me?
You may be a candidate for endovascular therapy if:
- You have leg pain worsened with activity and relieved with rest
- You have a leg or foot wound which is not healing
Key Advantages
Endovascular treatments are a safe treatment option and like other minimally invasive procedures have significant advantages over open surgery.
Benefits
- Extensive research demonstrating effectiveness for many types of PAD
- Same day procedure
- No general anesthesia required
- Short recovery time
- Reduce risk of limb loss
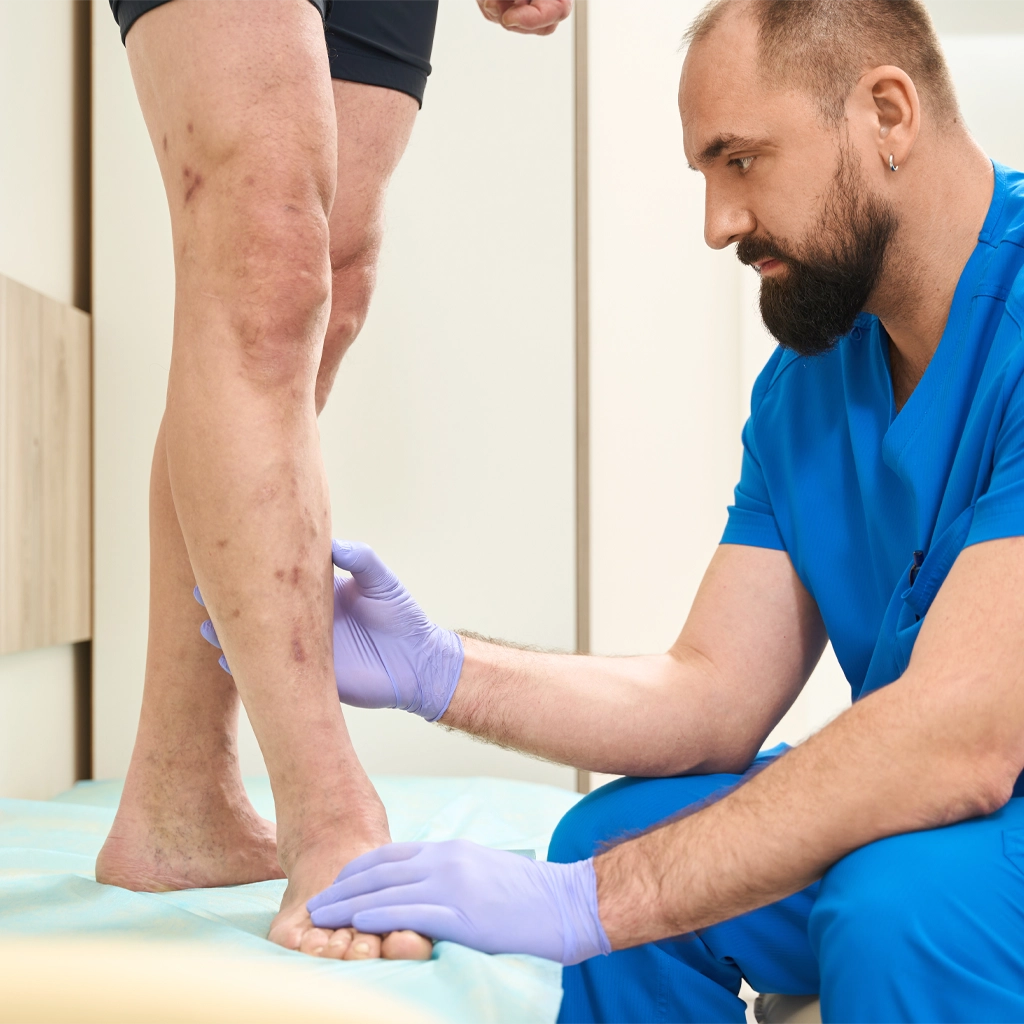
Risks
Although complications of endovascular therapies are rare, any medical procedure carries some degree of risk. Despite the low risk factor, it is important to understand the potential complications associated with PAD treatment. These include:
- Leakage of blood at the puncture site
- Blood clot or calcification blocking a different part of the body
- Injury to blood vessels
- Limb loss – rare
Other Treatment Options
Medical treatments
Many medications such as cholesterol lowering agents, aspirin, blood thinning agents, and/or clot prevention agents may be used to reduce the risk of minimally invasive therapies or surgery
Surgical treatments
Open surgical treatments as arterial bypass surgery is performed to create a path around the blocked artery using a blood vessel from another part of the body or a synthetic vessel. These procedures often require hospitalization and a long recovery time. Surgical treatments are often performed if minimally invasive therapy is not amenable or fails.
Other Conditions and Treatments
- Aortic aneurysm
- Renal artery atherosclerosis
- Carotid artery atherosclerosis